Implementing Measurement-Based Care: Practical Strategies from TLC Wellness and Zócalo Health
Measurement-Based Care (MBC) is no longer just a “nice-to-have” in behavioral health. It’s now recognized by accrediting bodies like the Joint Commission and CARF as a core component of high-quality, evidence-based care, and organizations are increasingly relying on MBC data to drive grant funding and value-based contracting opportunities. For many providers, the question is no longer about whether to implement MBC, but how to do it in a way that is practical, sustainable, and truly improves client outcomes.
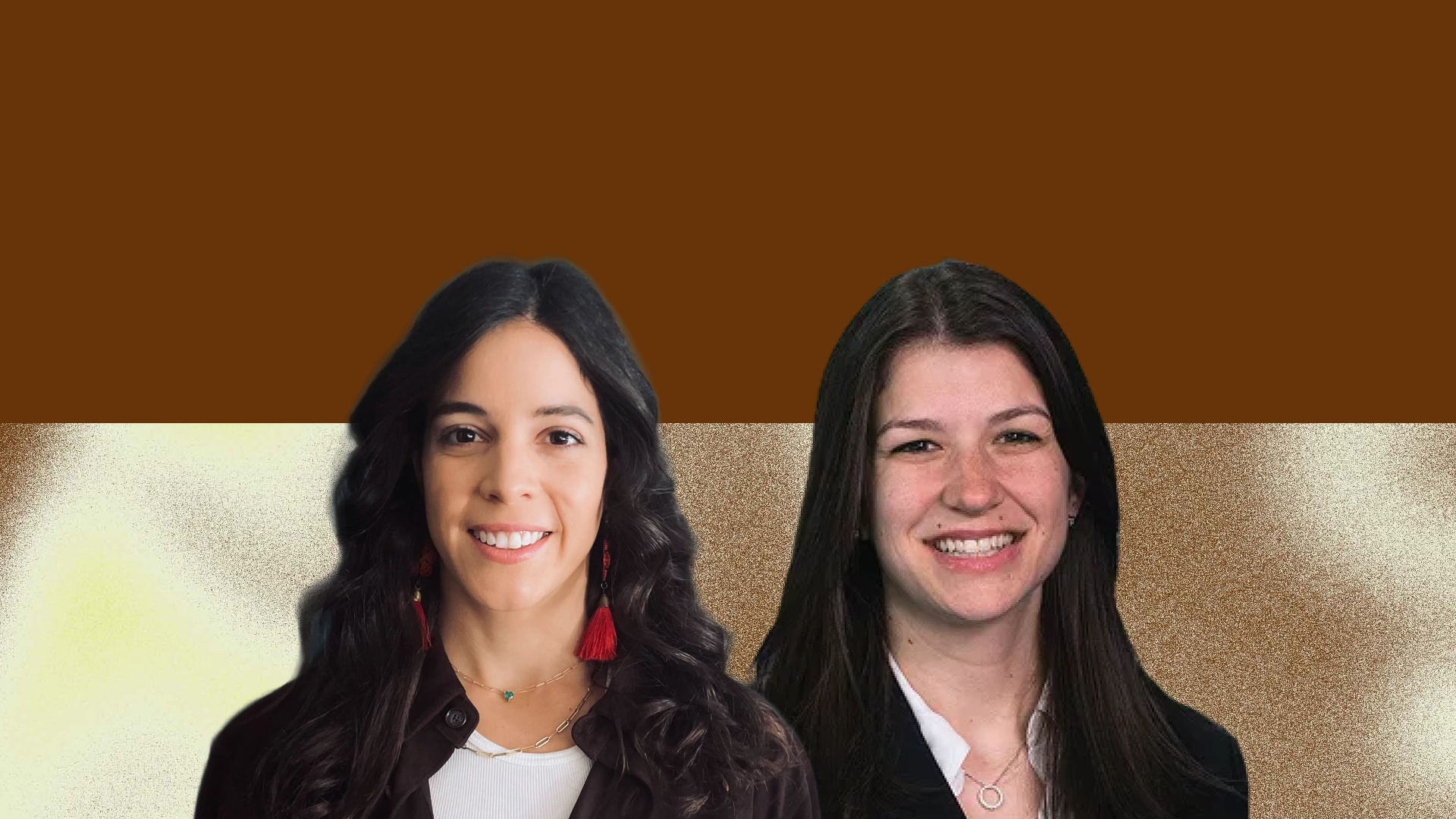
In a recent educational session, Carly Pointet, Customer Success Lead at Greenspace Health, sat down with two incredible behavioral health leaders:

Emily Gatto, Senior Vice President & Director of TLC Wellness at The Lincoln Center for Family and Youth.
TLC Wellness is an outpatient program built out of The Lincoln Center for Family and Youth, founded to meet the need for accessible behavioral health services within the community. They deliver high-quality, relationship-centered care with diverse clinical modalities and a strong commitment to accessibility.

Sophia Pages, Head of Behavioral Health at Zócalo Health.
Zócalo Health is a virtual, integrated primary care program serving primarily Spanish-speaking communities. Through evidence-based, comprehensive care services, they improve access to high-quality care for communities who face some of the largest detection and treatment inequities in behavioral health.
Leveraging Greenspace’s implementation framework, they walked through their own journeys with MBC implementation in 5 steps: Their ‘Why’ for MBC, workflow design, selecting assessments, training clinicians, and how they leverage data.
This article revisits the powerful insights discussed, featuring clips directly from the session, to outline how two different organizations can approach MBC and the lessons learned along the way. Whether you’re just thinking about MBC, or actively rolling it out, this guide will offer concrete strategies to fit the unique needs of your organization, your clinicians, and the clients you serve.
1. Identifying and Remembering Your ‘Why’ Behind Measurement-Based Care
A critical first step to implementation is identifying and outlining your ‘Why’ for implementing MBC. Your ‘Why’ will serve as the foundation of your implementation, helping to inform and guide how you approach the rest of the 4 stages. Before either organization chose measures or started leveraging data, they anchored their MBC implementations in a clear purpose.
Zócalo Health: Closing Detection and Treatment Gaps
Sophia highlighted several realities that shaped their reason for adopting MBC:
- In many community settings, over 60% of Latino adults are never screened for depression and anxiety.
- White adults are screened at nearly twice the rate of many minority groups.
- Only about one in three Black and Hispanic adults with a mental health condition receive any treatment, and many who are referred never make it past the first appointment.
For Zócalo, MBC became a non-negotiable tool to systematically identify behavioral health needs at every point and ensure that inequities were visible within their own data. Understanding their clients’ journeys and challenges was critical to understanding why members disengage, how to support them more effectively, and ultimately, deepen their engagement in care long term.
TLC Wellness: The Missing Puzzle Piece
Emily described MBC as the puzzle piece they were missing in their existing workflow that would help them achieve their broader organization-level goals. They were looking for a tool that would help them:
- Create a shared language across clinicians
- Bring clarity to treatment planning and progress tracking
- Make progress visible to youth, parents, and adults they serve
- Enable earlier detection of risk, including safety concerns that might only surface through structured screening
- Provide quantitative outcomes they could share with schools, stakeholders, and the broader community
- Strengthen supervision and clinical oversight
As Emily explains in the following clip, MBC helps clients visualize their progress, increasing engagement by providing a tangible way for them to understand their care journey.
MBC enabled them to enhance the experience of clients in care, while also leveraging that data to drive program improvement, funding advocacy, and enhanced clinical supervision.
2. Structuring Your Workflow
After identifying your why, the next step in implementation planning is structuring your workflow in a way that seamlessly embeds MBC into existing processes. At this stage, it’s imperative that the goals of your implementation are clearly outlined and how MBC will be integrated into every stage of the care process. Determining how clients will be added, how assessments will be completed (whether in session, via remote delivery, or in the waiting room by Kiosk), how often, and how clinicians should be leveraging results in session—and making those decisions based on your unique setting, programs, and population—will ensure your implementation enhances the clinical experience, without unnecessary burden for clinicians and clients.
Both organizations emphasized that MBC succeeds when it is embedded in workflows, rather than viewed as an additional task.
Zócalo Health: Universal Screening and Integrated Dashboards
Zócalo’s first structural decision was to implement universal screening, meaning every patient entering their clinic is screened using the same standardized set of measures. They also embed assessments into intake and follow-up workflows, so that they occur automatically and do not require additional action by the clinician.
With Greenspace, they were able to configure automatic reminders and cadences for both clinicians and clients, further reducing administrative work. Additionally, they have access to integrated dashboards (such as the Caseload Assistant) that provide a shared view across their multidisciplinary team, enabling them to detect patients who are deteriorating or stagnating in their care earlier, and identify patients who need to be prioritized or scheduled for a more intensive follow-up.
When designing their workflows, flexibility and accessibility were important factors at Zócalo. Taking into consideration the unique needs of their patients, which includes monolingual Spanish speakers, unhoused or older adults, and people without reliable smartphone or internet access, they offered flexible options to cater to the needs of their community. Through Greenspace, they were able to offer validated assessments in different languages, and the option to complete assessments at home, prior to sessions, at the beginning of sessions by kiosk, or led verbally by clinicians.
TLC Wellness: Addressing Clinicians’ Challenges
For TLC Wellness, their focus was on respecting clinician capacity and reducing administrative friction.
To address these needs, they designed their workflow around the needs of clients and their clinicians first. Every new client over the age of 12 at TLC Wellness completes their initial intake through the EHR, in addition to two baseline measures: the PHQ-9 (depression) and GAD-7 (anxiety). TLC intentionally doesn’t introduce a new platform at first interaction, in order to ease clients into their treatment journey.
Emily and her team wait until the first clinical session to introduce Greenspace and MBC. This way, their clinician can lead the conversation in a collaborative way, clearly framing the measures as tools that empower them in care, support clinical judgement, and help guide sessions.
They also discuss how assessments will be administered, giving clients the option to complete measures at home before sessions, independently at the beginning of the session, or together during the session. Emily emphasizes that the client’s preferences are always factored into the structure to encourage active participation and engagement in their care. TLC Wellness automates assessment reminders and notifications using Greenspace whenever possible, to ensure assessments are sent out on a regular cadence without adding manual steps for clinicians.
3. Selecting Responsive Measures
The variety and number of assessments you choose to assign to clients will depend on a number of factors, including the population you serve, programs offered, languages, and presenting symptoms.
When it comes to choosing assessments that accurately reflect the needs of each community, both organizations found a balance between assigning a core battery of measures, and layering in clinical judgement and flexibility to target more specific needs.
Zócalo Health: Validated, Culturally-Responsive Tools
At Zócalo Health, given that they work with primarily Spanish-speaking clients, language validity and cultural relevance were central considerations when choosing measures. They prioritized a small set of assessments with clear interpretability, strong evidence, and high-relevance to target a wide range of symptoms and reliably track progress over time.
Their core set, administered to every new client at entry point, includes the PHQ-9 for depression, GAD-7 for generalized anxiety, and PREPARE for social needs. The PHQ-9 and GAD-7 are administered at regular intervals for clients presenting with behavioral health needs, and PREPARE is administered every six months.
As Zócalo continues to grow and broaden their capabilities, Sophia plans to build a more robust library of Spanish and English validated assessments to better align with specific diagnoses and the unique needs of each and every client.
TLC Wellness: Baseline Measures and Clinician Flexibility
Similarly, TLC Wellness also uses the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 as baseline screening tools, along with a therapeutic alliance measure. As Emily shares in the following clip, regularly monitoring therapeutic alliance helps clinicians strengthen engagement and see whether a particular client-clinician match is a great fit.
Beyond the core battery, clinicians are encouraged to use their clinical expertise and judgement to add tools based on their specialties and clients’ challenges, goals, or presenting symptoms. Emily shared common assessments added on by clinicians, including OCD measures, the Vanderbilt for suspected ADHD in children, tools that address trauma-specific challenges, and additional screening tools in collaboration with their clinical psychologist.
4. Training Staff and Building Buy-In
Beyond technical workflows and measure selection, the way MBC is framed and introduced to clinicians and staff has a substantial impact on adoption. A recurring theme from both speakers was the importance of framing MBC as a core organizational practice that is integrated into the way care is delivered, and offering ongoing support to maintain momentum long term.
Zócalo Health: Embedding MBC into the Care Model
Sophia built the Behavioral Health program at Zócalo health with MBC in mind, making it a core, non-optional part of their care model from day one.
Zócalo introduced MBC as a practice that will enhance clinician’s skills and expertise by supporting clinical decision-making, strengthening supervision, and paving the way for more collaborative care. Zócalo incorporated ongoing training and resources to support clinicians as they gain confidence integrating MBC into their clinical care process. They also added MBC into KPIs and performance reviews, with an emphasis on clinician engagement with the platform, instead of whether every client is completing every measure.
Sophia emphasized that when clinicians understood they wouldn’t be penalized for client factors outside of their control, and had access to clear structures, dashboards, and ongoing support with interpreting and using data to inform care, they were able to see stronger buy-in across the organization.
TLC Wellness: Pilot Groups and MBC Champions
At TLC Wellness, Emily views MBC as a clinical tool that is designed to enhance care, which is why it’s embedded into weekly supervision where clinicians review trends, interpretations, and decisions together. Emily described how keeping MBC central to conversations helps clinicians collaborate and understand its value in care, empowering them to identify deterioration earlier, support their clinical judgement, and quantify impact.
Emily shared the value they drew from starting with an MBC pilot program and identifying early clinician champions, especially being a larger organization. This way, their champions could become peer leaders and resources for others when questions or concerns around MBC arose, which helped support an effective adoption across the rest of the organization.
In the clip below, both Sophia and Emily share how they maintain the momentum around MBC by keeping it a part of ongoing conversations and weekly routines, allowing clinicians to regularly review and discuss the impact of using MBC.
5. Leveraging Data Beyond the Session
The final component to building a successful, sustainable MBC workflow is to determine how you will leverage your data. Both Zócalo Health and TLC Wellness use MBC data beyond individual sessions to expand the impact of their programs.
Zócalo Health: Closing Loops and Care Gaps
With Greenspace’s dashboards providing insights at the individual client level and population-level trends, Zócalo is able to:
- Identify low utilizers and disengaged members
- Track patients who frequently use the emergency department for behavioral health crises
- Monitor how patients are progressing over time, and how engaged they are in their care
This visibility allows them to demonstrate to health plans and investors the effectiveness of their services, and how their clients are achieving better outcomes, enhanced engagement, and meaningful progress in their care. Additional data and insights also help clinicians reassess clients at key milestones to identify any potential new or evolving behavioral health needs, flag individuals presenting symptoms for more intensive support, and re-engage patients already in their ecosystem who may need additional support.
TLC Wellness: Demonstrating Community Impact
Beyond using MBC data to inform treatment planning, goal-setting, progress tracking, and decision-making in sessions, TLC Wellness leverages the Greenspace platform to:
- Demonstrate their commitment to enhancing quality and outcomes
- Support program development based on real outcome trends
- Communicate impact to schools, nutrition programs, and community partners
- Incorporate results and key statistics in marketing materials and year-end reports
In the following clip, Emily outlines how collecting impact data is a core component of how they demonstrate their impact and achievements to their community.
Wrapping Up: A Practical Roadmap for Implementation
TLC and Zocalo health are excellent examples of how MBC can be seamlessly embedded across an organization in a way that complements your population and their needs, the programs you offer, and existing clinical workflows. Similar to their implementation journeys, organizations considering MBC should begin by outlining these 5 key components:
- Define your why: Anchor MBC in a clear purpose.
- Choose your core measures: Start with a set of assessments that are relevant and validated for the community you serve, and add additional or complimentary measures as needed.
- Embed workflows in existing processes: Decide when assessments are sent or administered, who is responsible at each step, and how results are reviewed and brought into sessions.
- Invest in training and culture: Plan for ongoing training, supervision time focused on using data, and frame MBC in a way that supports clinicians.
- Decide how you’ll use the data: Determine how individual client data will be used to inform treatment planning and discussions, and how aggregate data will be used in communications with funders, partners, and the community.
From there, implementation becomes less about “adding one more thing” and more about evolving how care is delivered—making progress visible, strengthening engagement, and aligning behavioral health with the same data‑driven standards seen across the rest of healthcare.
Interested in learning more about how to implement MBC at your organization? Schedule a call with an implementation specialist or reach out at info@greenspacehealth.com.